As we move through the world, we’re surrounded by a symphony of sounds that provide vital clues about our environment. Our brains process these sounds, transforming them into actionable insights that help us navigate our surroundings. Fortunately now, thanks to the power of machine learning, we have the ability to undertake noise measurement in ways that far surpass human capabilities.
With AI, we can automatically analyse and quantify sound at a scale and level of precision that was previously unimaginable. From the chirping of birds to the hum of traffic, every sound can be measured and used to generate valuable insights about the world around us.
AI for noise measurement has numerous benefits that standard sensors just can’t offer. In this article, we will take you through the ins and outs of noise measurement with machine learning. We will also share Gemmo’s new API for noise measurement.
What is Noise Measurement?
Noise measurement is the process of measuring the level of sound in a given environment. It is an essential tool that helps us understand the impact of sound on human health and the environment.
As well as this, it is also necessary for maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements. Once we are able to detect and measure harmful sounds, we can take the necessary steps to protect human hearing.
Over 20% of the EU’s population are exposed to harmful noise for a prolonged period of time. In light of this, the vitality of noise measurement cannot be stressed enough.
How is Noise Measured?
The process of measuring noise is relatively simple; we utilise sensors specifically designed to detect sound levels in a designated area. Noise sensors are specifically designed to measure the levels of sound in a given area.
In order to gather data on noise pollution levels, specialists purposefully place them in high-traffic areas, such as near roads, airports, and construction sites.
Environmental sensors work by detecting sound waves and converting them into electrical signals. Analysing these signals then determines the frequency and strength of the sound, which assists in pinpointing the source of the noise pollution.
The most common type of sensor used for noise measurement is a microphone sensor. This type of sensor is similar to the one in your phone or laptop, and it works by detecting sound waves and converting them into electrical signals.
The microphone sensor contains a small diaphragm that vibrates in response to sound waves. To determine the sound level, these vibrations are converted into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and examined. This process happens rapidly, allowing the sensor to provide real-time data on noise levels.
The Problem: Times are Changing
Over the past decade, noise sensors have made significant strides in accuracy and functionality. However, the increasing prevalence of AI technology has made even the most advanced sensors appear outdated and excessively manual.
The current process of manually listening to recorded audio files, identifying sounds, and categorising them is a time-consuming and tedious task. As the market demands innovation and automation, it has become essential to integrate AI into sensors to keep pace with the evolving technology landscape.
With AI becoming increasingly prevalent in people’s daily lives, incorporating it into noise sensors is crucial to adapt.
The Solution? AI-Powered Sensors for Noise Measurement
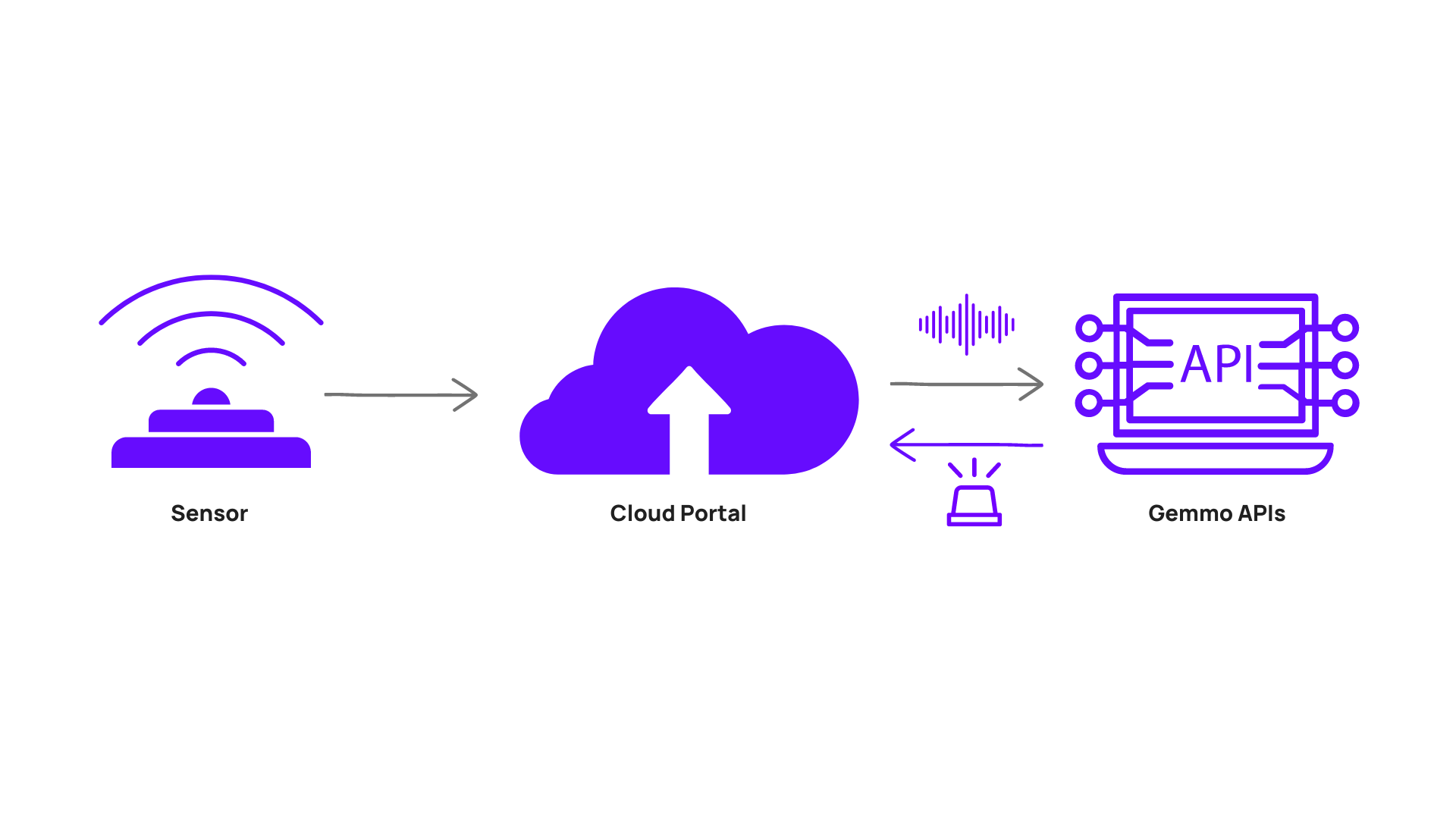
The solution lies in AI for noise analysis. Machine Learning algorithms have the ability to label sound clips with tags relevant to the context of the use of the noise monitoring device.
For example, construction sites would have different tags for impact sounds, vehicles, natural sounds, human voices, tools, and sirens. Integrating this feature into sensors would make them more reliable, capable, and accurate.
AI-powered sensors and microphones can detect sound waves, differentiate between different types of sounds, and detect patterns and anomalies in sound data that are difficult for humans to recognise. This means that the data collected by AI-powered sensors and microphones are much more precise and reliable.
AI makes real-time monitoring achievable, enabling immediate intervention in an instance of high noise levels. On top of that, comprehensive data analysis can provide insights into the impact of noise pollution on human health and the environment, helping policymakers to develop appropriate mitigation strategies.
By integrating APIs, hardware manufacturers can leverage trusted AI technology to enhance the accuracy and automation of sensors, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Gemmo’s API: Noise Source Identification in Online Reporting Platforms
The Gemmo Noise API goes beyond just labelling sound clips with relevant tags. It also offers noise source attribution, which is useful for quickly discarding irrelevant noise clips and detecting acoustic events. Examples of such events include blasts, rain, and wind.
This feature is particularly useful in a number of ways:
- for removing background noise from large audio clips automatically,
- identifying sparse, rare sound events of interest, such as blasting, piling, or engine spinning,
- for sound retrieval.
With sound retrieval, users can find sound events similar to the ones already identified, making it easier to track and analyse trends over time.
How Does it Work?
Monitoring noise levels is essential for ensuring environmental safety. This is especially vital in noise pollution-prone areas like construction sites and roadsides.
Fortunately, sensors can assist in achieving this. Placed strategically on-site, these sensors detect and log sounds once they cross a certain decibel level.
However, imagine hundreds of sensors on several roadsides all operating at the same time. That’s a huge amount of data for humans to listen through and determine if the detection is correct.
Our innovative system automates this entire process, from sound detection to analysis, leaving no room for human error. Once a noise sample is recorded, it’s sent to our remote server for processing.
Within seconds, our API classifies the sound and assigns it a probability level. For example, it can classify an ambulance siren with 90% accuracy.
Final Thoughts on AI for noise measurement
The capabilities of AI are transforming the noise measuring industry. With our Gemmo Noise API, we’re automating the process of sound detection and analysis, leaving no room for human error. It’s like having a team of noise detectives at your fingertips, ready to identify every sound and provide valuable insights into the impact of noise pollution on human health and the environment.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Latest Posts